
What is Breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding, also called nursing, is the process of feeding a mother’s breast milk to her infant, either directly from the breast or by expressing (pumping out) the milk from the breast and bottle-feeding it to the infant. Breastfeeding and breast milk provide an infant with essential calories and nutrients, including macronutrients (fat, protein, and carbohydrates) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Colostrum, the yellowish, sticky breast milk produced at the end of pregnancy, is recommended by WHO as the perfect food for the newborn, and feeding should be initiated within the first hour after birth. Exclusive breastfeeding is recommended up to six months of age, with continued breastfeeding along with appropriate complementary foods up to two years of age or beyond.
Signs that Mother’s Milk is Insufficient
Most new mothers worry if they have got enough breast milk for their baby. In most cases, there is no reason to worry. However, keep an eye out for the following signs that hint your baby isn’t getting enough milk or that it isn’t nutritious enough:
Slow or no weight gain
Insufficient wet or dirty nappies

Dehydration

Falling sick often

Developmental delays
Low in energy
Low body temperature
Benefit of Breastfeeding
For the Baby
- It supplies all the necessary nutrients in the proper proportions.
- It protects against allergies, sickness, and obesity.
- It protects against diseases, like diabetes and cancer.
- It protects against infections, like ear infections.
- It is easily digested – no constipation, diarrhoea or upset stomach.
- Babies have healthier weights as they grow.
- Breastfed babies score higher on IQ tests.
For the Mother
- Have a reduced risk of Type 2 Diabetes
- Reduces risk of cancers, especially breast cancer
- Helps you lose weight
- Strengthen the bond with their children
- Lowers Risk of Depression
- Lowers Risk of Disease
- Saves Time and Money on feeding formula
Misconceptions about low milk supply
The following are all perfectly normal and are not signs of a poor milk supply:
- Your baby wants to feed frequently
- Your baby doesn’t want to be put down
- Your baby is waking in the night
- Short feeds
- Long feeds
- Your breasts feel softer than they did in the early weeks
- Your breasts don’t leak milk, or they used to leak and have stopped
Reason for low milk supply
Some of the reasons for low breast milk supply could be:
Breast milk coming in late (delayed onset of lactation)

Poor breastfeeding management

Baby’s breastfeeding skills

Nipple Shape challenges
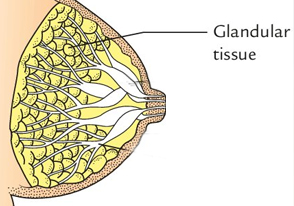
Insufficient glandular tissue
Breast surgery or trauma

Hormonal or endocrine disorders

Diet Choices

Medications

Pollution

Lack of Confidence & Interest
Important to Note
Why should India promote breastfeeding?
- Reduces Under-5 Mortality by 13%
- Prevents 39,00,000 episodes of diarrhea
- Prevents 34,36,560 episodes of pneumonia
- Reduces Obesity by 26%
- Prevents 4,915 deaths due to breast cancer
- Reduces type-2 diabetes by 35%
- Improves IQ in children by 3 points


Risk Factor For Non-breasted Children
- Higher Chance of Obesity
- Risk of Juvenile Diabetes
- Risk of Asthama & Allergy
- Risk of Childhood Cancers
- Risk of Heart disease
- Risk of Multiple Sclerosis
- Risk of Digestive Diseases
- Comparatively less Cognitive Development


BREASTFEEDING: THE ULTIMATE LOVE & NOURISHMENT
Mother’s Milk lays the strongest foundation for the newborn baby’s health, developing immunity and ensuring much-needed nourishment. KsheerVardhini™ granules are made by taking inspiration from the grandmother’s age-old recipes and supported by the research and findings of modern times.
